In che modo il kit di catetere venoso centrale raggiunge scopi medici attraverso la sinergia di vari componenti?
Analisi dei componenti principali del kit
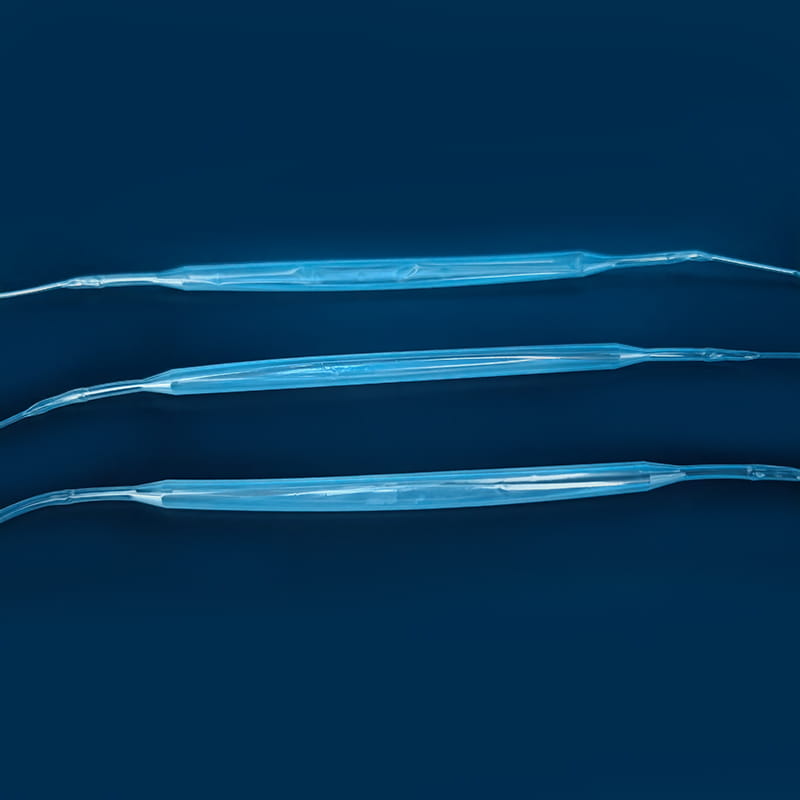
IL kit di catetere venoso centrale Contiene una varietà di componenti chiave, ognuno dei quali svolge un ruolo unico e insostituibile nell'intero processo di operazione medica. Il primo è il catetere venoso centrale, che è il componente centrale del kit ed è il canale che collega la vena centrale fuori dal corpo e all'interno del corpo. Il suo materiale è generalmente realizzato in poliuretano o silicone di livello medico. Tali materiali hanno una buona biocompatibilità e possono ridurre efficacemente il rifiuto del corpo di corpi estranei e ridurre il rischio di complicanze come l'infezione. Diversi tipi di cateteri venosi centrali hanno le proprie caratteristiche nella struttura e nella funzione. I cateteri a lume singolo sono adatti per esigenze di trattamento singolo, mentre i cateteri a doppio lumen o multi-lumen possono eseguire una varietà di operazioni mediche diverse contemporaneamente, come l'infusione, la raccolta del sangue e la somministrazione di farmaci, che migliora notevolmente l'efficienza e la convenienza delle operazioni mediche. In termini di design, alcune superfici del catetere sono trattate con rivestimenti speciali per migliorare ulteriormente le proprietà anti-trombotiche; Alcuni sono anche contrassegnati con scale per facilitare il personale medico per comprendere accuratamente la profondità di inserimento.
IL cannula plays a pioneering role in the central venous catheter kit. When performing a central venous catheter insertion operation, the cannula is first used for percutaneous puncture into the vein. Its needle tip adopts a bevel cutting process. This design is sharp and precise, and can quickly and accurately penetrate the skin and vein wall with minimal resistance, opening a channel for the entry of subsequent components. The needle core and outer sleeve of the cannula needle are closely matched. When the cannula needle successfully enters the vein, the inner needle core is removed through a special separation mechanism, and the outer sleeve with a certain hardness and flexibility will remain in the vein as a guide channel for subsequent guide wires and other components to enter. To ensure the accuracy of puncture, some cannula needles are also equipped with ultrasound guidance adapters, which can be used with ultrasound equipment to observe the puncture path and blood vessel status in real time.
IL guidewire is a key tool for precise positioning and guidance in the central venous catheter kit. After the cannula needle establishes the initial channel, the guidewire will be sent into the vein through the cannula. The outer layer of the guidewire is usually woven from medical-grade stainless steel wire, and the inner layer is a nickel-titanium alloy core. This structure gives the guidewire good flexibility and maneuverability. Doctors can use the J-shaped or straight head design of the guidewire tip to flexibly turn and guide it in the blood vessel through in vitro operation, and accurately send it to the target position. Some high-end guidewires also have a hydrophilic coating, which becomes lubricated after contact with blood, further reducing friction damage to the inner wall of the blood vessel. The existence of the guidewire makes the insertion path of the central venous catheter clearer and more controllable, laying a solid foundation for the smooth insertion of the subsequent catheter.
IL role of the dilator in the central venous catheter kit should not be ignored. Since the diameter of the vein is relatively thin, and the central venous catheter needs to be smoothly inserted, it is necessary to properly dilate the vein. The dilator usually adopts a conical or cylindrical design, and the material is mostly medical-grade polyethylene. It can enter the vein along the guidewire and expand the channel of the venous puncture site by gradually expanding. During the expansion process, the smooth surface treatment and gradual caliber design of the dilator can reduce damage to the venous tissue while ensuring effective expansion. For special patients, such as those with thin blood vessel walls or sclerosis, there are also special controllable dilators available, and doctors can accurately adjust the expansion strength and range according to actual conditions.
IL peelable sheath is an important part of the central venous catheter kit to ensure the safe insertion of the catheter. After the dilator completes the dilation of the vein, the peelable sheath will be sent into the vein along the guidewire and dilator. The peelable sheath consists of two symmetrical half sheaths connected by a special locking structure in the middle. When the peelable sheath reaches the appropriate position, the central venous catheter will be inserted into the vein through the sheath. At this time, the medical staff will separate the peelable sheath from the middle lock and remove it from the body through a specific operation technique, while the central venous catheter will be left in the vein. This unique design not only ensures the smooth catheter insertion process, but also avoids unnecessary damage to the vein and catheter. To prevent accidental scratches on the surrounding tissue when the sheath is peeled off, the edge of the sheath is specially rounded and blunted.
IL fixing device plays a role in stabilizing and fixing the catheter in the central venous catheter kit. In order to ensure that the central venous catheter can maintain a stable position in the patient's body for a long time without displacement or falling off, fixing devices such as sutures, sterile dressings or special catheter fixers will be used to fix the catheter to the patient's skin. The suture fixation method is suitable for patients with long-term catheterization. The catheter is fixed to the skin tissue through delicate suturing operations; the sterile dressing is breathable, waterproof and antibacterial, and can effectively protect the puncture site; the dedicated catheter fixator is made of medical-grade silicone or polymer materials, and can be personalized according to the patient's skin morphology and catheter model through an adjustable buckle design. Appropriate fixation can not only ensure the normal function of the catheter, but also reduce the discomfort and potential risks caused to the patient by the movement of the catheter.
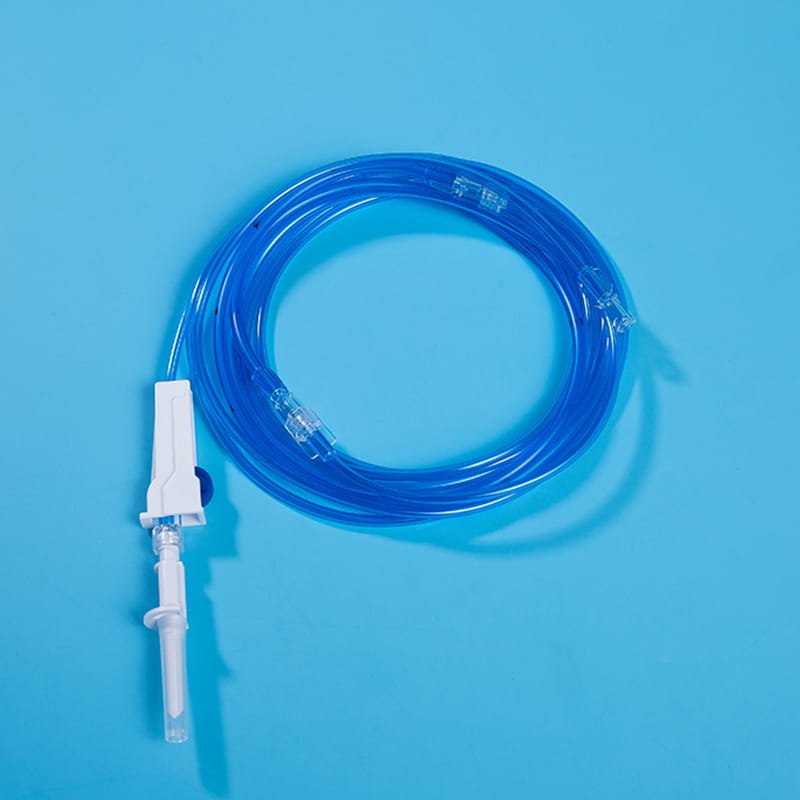
IL interface for external connection is the bridge between the central venous catheter and external medical equipment. Through these interfaces, the central venous catheter can be connected to infusion sets, syringes and other equipment to achieve various medical operations such as infusion, drug administration, and blood collection. The design of these interfaces has good sealing and compatibility, and common ones include Luer connectors and needleless infusion connectors. The Luer connector is connected by threads to ensure a tight connection without leakage; the needleless infusion connector adopts a diaphragm design, which can complete the infusion operation without acupuncture, reducing the risk of infection. At the same time, some interfaces also have anti-backflow function to prevent blood from reflux and blocking the catheter, and support multiple devices to be connected at the same time to meet complex clinical needs.
Ampia gamma di scenari di applicazione clinica
Nelle applicazioni mediche reali, gli scenari di utilizzo dei kit di catetere venoso centrale sono molto ampi. Nel campo della terapia intensiva, per i pazienti con condizioni critiche che necessitano di una grande quantità di infusione e frequenti farmaci, i cateteri venosi centrali possono fornire un canale di infusione rapido e stabile per soddisfare le esigenze dei pazienti di liquidi e farmaci. Prendendo i pazienti con shock settico come esempio, durante il processo di salvataggio, una grande quantità di fluido cristalloide, fluido colloide e farmaci vasoattivi devono essere integrati in un breve periodo di tempo. Il catetere venoso centrale può garantire che questi fluidi e farmaci entrino rapidamente nella circolazione sanguigna e correggano rapidamente lo stato di shock. Allo stesso tempo, il monitoraggio emodinamico può anche essere eseguito attraverso il catetere venoso centrale. Il medico collega il sensore di pressione all'interfaccia del catetere per ottenere parametri come la pressione venosa centrale e la pressione del cuneo dell'arteria polmonare in tempo reale, il che aiuta i medici a comprendere la funzione cardiaca del paziente e lo stato di circolazione del sangue in tempo reale e fornisce una base importante per la formulazione di piani di trattamento accurati.
Nel trattamento del tumore, molti farmaci chemioterapici sono altamente irritanti per i vasi sanguigni e la somministrazione attraverso le vene periferiche può causare complicanze come la flebite. Il kit di catetere venoso centrale può posizionare un catetere nella vena centrale, consentendo ai farmaci chemioterapici di entrare direttamente nei grandi vasi sanguigni ed essere rapidamente diluito, riducendo così l'irritazione ai vasi sanguigni, riducendo la probabilità di complicanze e migliorando la tolleranza al trattamento dei pazienti e la conformità. Ad esempio, i pazienti con carcinoma mammario che ricevono farmaci chemioterapici altamente irritanti come la doxorubicina possono usare cateteri venosi centrali per evitare efficacemente gravi conseguenze come la necrosi cutanea e l'ulcerazione tissutale causata dalla stravasa di farmaci. Allo stesso tempo, per i pazienti che hanno bisogno di chemioterapia a lungo termine e multipla, i cateteri venosi centrali riducono il dolore delle forature ripetute e migliorano la continuità del trattamento.
Inoltre, nella terapia di supporto nutrizionale, i cateteri venosi centrali possono essere utilizzati per il supporto al nutrizione parenterale totale per i pazienti che non possono assumere una nutrizione sufficiente attraverso il tratto gastrointestinale, come i pazienti con coma a lungo termine e ustioni gravi. Dare una soluzione nutritiva ad alta concentrazione e ricca di calorie attraverso la vena centrale può soddisfare le esigenze del corpo del paziente per i nutrienti e promuovere il recupero del paziente. Prendendo i pazienti con ustioni estese come esempio, la loro funzione gastrointestinale viene soppressa a causa del trauma e non possono digerire e assorbire il cibo normalmente. Al momento, la soluzione nutritiva all-in-one contenente aminoacidi, emulsione di grasso, glucosio e altri ingredienti viene somministrata attraverso il catetere venoso centrale per mantenere l'equilibrio dell'azoto del paziente, riempire l'energia richiesta dal corpo e accelerare la guarigione delle ferite. Allo stesso tempo, il personale medico può anche monitorare gli elettroliti del paziente, la glicemia e altri indicatori attraverso il catetere venoso centrale e regolare il piano di supporto nutrizionale in tempo.
Procedure operative rigorose e standardizzate
IL operating procedures of the central venous catheter kit need to strictly follow the specifications and standards. Before the operation, the doctor needs to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition, including the patient's age, weight, underlying diseases, coagulation function, etc., and select the appropriate puncture site and central venous catheter type. Common puncture sites include the internal jugular vein, subclavian vein and femoral vein. Different sites have their own advantages and disadvantages, and they need to be carefully selected according to the specific situation of the patient. At the same time, detailed explanations and communication should be given to the patient, and the patient should be informed of the operation process, possible risks and key points of cooperation to obtain the patient's cooperation. During the operation, the principle of aseptic operation must be strictly followed. The puncture site must be disinfected with iodine more than three times, and the diameter of the disinfection range must not be less than 15 cm. A large sterile sheet must be laid to ensure that the entire operation is carried out in a sterile environment. Then follow the steps of trocar puncture, guide wire insertion, dilation with a dilator, insertion of a removable sheath, insertion of a central venous catheter, fixation of the catheter, and connection of an external interface. Taking internal jugular vein puncture as an example, under ultrasound guidance, after determining the puncture point, the trocar is inserted at an angle of 30-45 degrees. After seeing the blood return, it is confirmed that it is in the vein, and then the subsequent components are inserted according to the process. After the operation is completed, the patient needs to be closely observed and cared for, and the patient must be monitored for complications and treated in a timely manner. This includes observing whether the puncture site is red, swollen, or exuded, and changing the dressing regularly; monitoring the patient's body temperature, blood routine, and other indicators to determine whether an infection has occurred; evaluating the function of the catheter to ensure smooth infusion, blood collection, and other operations.
Sfide e rischi affrontati
Sebbene i kit di catetere venoso centrale svolgano un ruolo importante nel campo medico, affrontano anche alcune sfide e rischi durante l'uso. L'infezione è una delle complicanze più comuni dei cateteri venosi centrali. Poiché il catetere viene lasciato nel corpo per molto tempo, è facile invadere i batteri e altri microrganismi, causando infezione locale o infezione sistemica. I batteri entrano principalmente nel corpo attraverso la colonizzazione della pelle nel sito di puntura, la contaminazione del connettore del catetere e la contaminazione del sistema di infusione. La trombosi è anche un problema che non può essere ignorato. Il catetere può stimolare l'endotelio vascolare nel vaso sanguigno, causando cambiamenti nella coagulazione del sangue, formando così un trombo. Una volta che il trombo cade, può causare gravi complicanze come l'embolia polmonare. Inoltre, problemi come il blocco del catetere e lo spostamento possono anche influire sul normale uso e effetto di trattamento del catetere venoso centrale. Il blocco del catetere può essere causato dalla deposizione di farmaci, dalla coagulazione del sangue, ecc.; Lo spostamento del catetere può essere correlato a fattori come un'attività impropria del paziente e una fissazione allentata.
For more information, please call us at +86-18913710126 or email us at .
Le procedure interventistiche vascolari sono parte integrante della moderna medicina cardiovascol...
Introduzione Tubo endobronchiale a lume singolo I dispositivi sono un...
Nella medicina moderna, i cateteri medici sono strumenti indispensabili utilizzati in una vasta g...
Nel settore sanitario, l’importanza di selezionare i materiali giusti per i dispositivi medici no...
Nell’era della medicina di precisione, un piccolo tubo spesso porta con sé il peso delle responsa...
Nell'assistenza sanitaria moderna, una gestione precisa dei fluidi è fondamentale per la sic...